This unusual cosmic object will help shed light on the process by which magnetic fields interact with the environment in nebulae formed by pulsars. Earth science already has, says Stanford University’s Niccolo Di Lalla, enough material to study the behaviour of super-energetic matter and antimatter particles around the pulsar. Moreover, researchers have already drawn an important conclusion – pulsars can act as natural particle accelerators.
Mia Harris
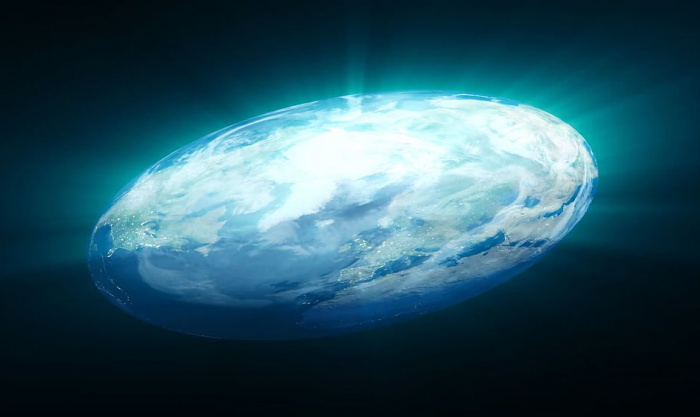
A flat Earth is not a myth, but a very likely past of our planet
It turned out that the formation of the planet under certain circumstances begins with the creation of a dust disc. It twists, because of which the matter begins to accumulate on the disc unevenly – less at the edge and more in the centre, near the axis of rotation. And then the poles. Thus, for some time the planet “blank” looks like a thick pancake, then begins to resemble a yule. The mass of matter in the centre grows and it becomes rounded, takes a close to spherical shape. However, this is just a hypothesis, we have yet to find such a flat planet.
Scientists have revealed the first cases of Alzheimer’s disease infection
Treatment with growth hormone from dead people combined with a fairly young age of development of the disease allowed scientists to conclude that Alzheimer’s disease in patients was not sporadic or hereditary in nature. They believe that its development is due to the transmission of a pathogenic form of beta-amyloid. At the same time, there is no risk of new cases of transmission of the disease in this way today due to the fact that therapy with growth hormone of cadaveric origin is no longer practised.
Scientists beat the temperature inside the Chicxulub crater after the dinosaur-killing asteroid hit
It is noted that the Chicxulub crater was formed when a 12-kilometre-long celestial body travelling at 43,000 km/h collided with our planet, creating a 200-kilometre-deep depression in what is now known as the Gulf of Mexico. Violent tsunami waves almost completely filled the crater with sediment within minutes to hours of impact.
A new method of determining a person’s geolocation by gadget has been created
As they said, thanks to this technology was determined the geolocation of a smartphone, removed by 7 metres, with an accuracy of 3 centimetres. According to the researchers, in the future such technology will allow to control the movement of robots and autonomous vehicles more accurately.
Stratospheric dehydration may prove to be an effective way to combat climate change
They also emphasised the importance of one region over northern Australia in controlling upward flows of air and water vapour. The researchers conjectured that if stratospheric water vapour was reduced in this small region, more release of infrared radiation into space could be achieved in this way.
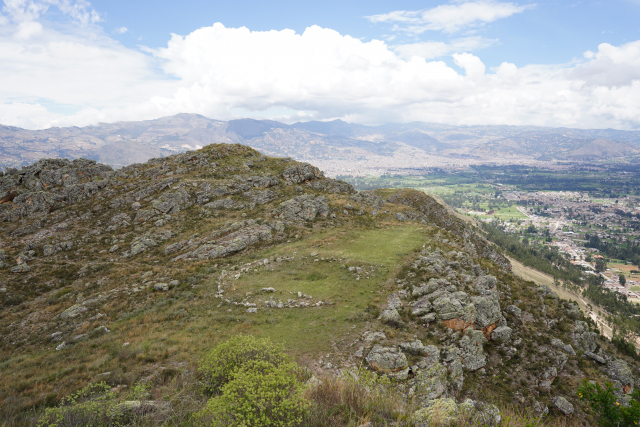
Archaeologists have found mysterious stone circles built before the Egyptian pyramids
Using radiocarbon dating, the researchers determined that the structure was erected about 4,750 years ago, which falls within the late ceramic period of Andean archaeology. As noted by experts, this structure was built about a century before the pyramids in Egypt and almost at the same time as Stonehenge in the UK.
Scientists attribute the structure to an example of monumental megalithic architecture, with the find representing one of the earliest examples of such architecture in the Americas.
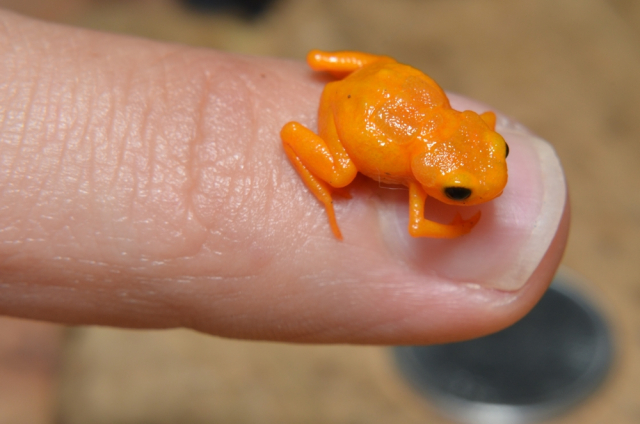
A toad from Brazil could be recognised as the smallest amphibian on Earth
And the fact that these ‘messages’ within the nerve circuits are cancelled by the anaesthetic clearly indicates the animal’s ability to feel the affective component of pain, i.e. excitement, mental pain, in addition to physical pain.
The results of this experiment raise ethical questions about how one should behave when keeping and researching cephalopods. Experts believe that the nervous system of octopuses and other molluscs actually has much greater potential than previously thought.
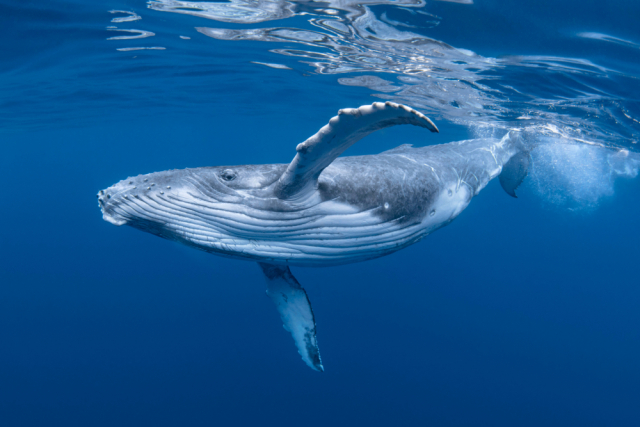
As a result, about 7,000 humpback whales disappeared over the next eight years, probably due to lack of food. Scientists emphasised that these animals are quite flexible in their diet, but when the entire ecosystem suffers, they suffer enormous damage. In addition, the experts pointed out that, in addition to the dead whales, there were many “skinny” individuals, which are more susceptible to diseases and worse at producing offspring.